Definition of Near Sightedness.
Near-sightedness is a typical vision condition in which close to objects show up clear yet protests farther away look hazy. It happens when the state of the eye — or the state of specific pieces of the eye makes light beams twist (refract) erroneously. Light beams that ought to be centered around nerve tissues at the rear of the eye (retina) are engaged before the retina.
Astigmatism as a rule creates during youth and puberty, and
it ordinarily turns out to be steadier between the ages of 20 and 40.
Near-sightedness will in general spat families.
A fundamental eye test can affirm myopia. You can make up
for the hazy vision with eyeglasses, contact focal points, or refractive medical
procedures.
Types of Myopia.
- Congenital Myopia
- Simple or Developmental Myopia
- Pathological Myopia
- Acquired Myopia
- Low myopia (generally less than 3 dioptres of myopia
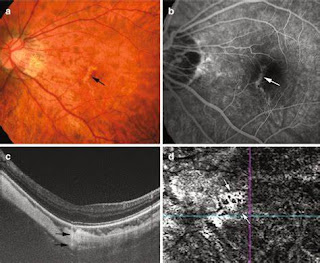
Pathologic near-sightedness is a significant reason for low vision and visual impairment around the world. Its social and financial weight has been shown by epidemiological examinations. There have been late advances in the grouping framework for nearsighted maculopathy that empowers clinicians to portray various sorts of injuries, including decorated fundus, diffuse/sketchy decay, macular decay, veneer breaks, choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and Fuchs' spot, in a normalized design. According to a restorative perspective, hostile to vascular endothelial development factor treatment has been laid out as the first-line decision for nearsighted CNV.
What are the symptoms of Myopia?
Astigmatism signs or side effects might include:
- Hazy vision while checking far-off objects out.
- The need to squint or to some extent close the eyelids to obviously see.
- Migraines
- Eye fatigue
Youngsters might experience issues seeing things on white
sheets or screen projections in the homeroom. More youthful kids probably won't
communicate trouble seeing; however, they might have the accompanying ways of
behaving that propose trouble seeing:
- Tirelessly squint
- Appear to know nothing about far-off objects.
- Squint unreasonably
- Rub their eyes regularly.
- Sit near the TV
Grown-ups with near-sightedness might see trouble perusing
road signs or signs in a store. Certain individuals might encounter foggy
vision in faint light, similar to evening time driving, regardless of
whether they see obviously in sunlight. This condition is called night
near-sightedness.
Near-sightedness is grouped into various sorts.
- Inherent Near-sightedness
- Basic or Formative Near-sightedness
- Neurotic Near-sightedness
- Obtained Near-sightedness
There is no effective, neighborhood, or foundational pharmacotherapy or medical procedure that is known to change actually the expansion in hub length and diminishing that happens in the sclera, choroid, and retina of eyes with pathologic near-sightedness.

Informative👍
ReplyDelete